A Comprehensive Guide to Electric Vehicle Chargers
FAQ
A Comprehensive Guide to Electric Vehicle Chargers
This document serves as an extensive guide to understanding electric vehicle (EV) chargers, covering various types, standards, charging speeds, and factors to consider when selecting the right charger for your needs. With the growing popularity of electric vehicles, it is essential to grasp the intricacies of charging technology to make informed decisions about home and public charging solutions.
Types of EV Chargers
Electric vehicle chargers can be broadly categorized into two main types based on the type of current they use:
- AC (Alternating Current) Chargers: These are the most common type of charger and use the same type of electricity as your home. AC chargers are generally slower than DC chargers and are ideal for home or workplace charging.
- DC (Direct Current) Fast Chargers: These chargers provide a much higher power output, allowing for much faster charging times. DC fast chargers are typically found at public charging stations.
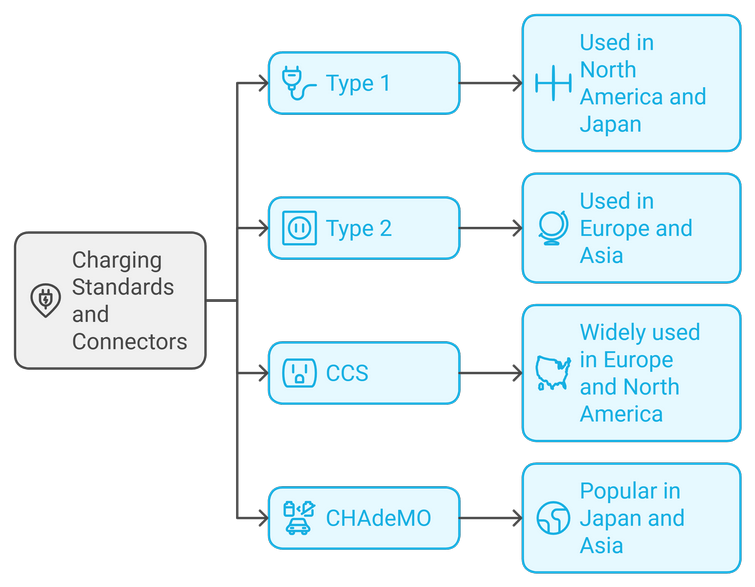
Charging Standards and Connectors
Different regions of the world have adopted different charging standards. Some of the most common ones include:
- Type 1: Commonly used in North America and Japan, Type 1 connectors are smaller and often used for slower AC charging.
- Type 2: More prevalent in Europe and Asia, Type 2 connectors are larger and can support both AC and DC charging.
- CCS (Combined Charging System): A combination of AC and DC charging, CCS is widely used in Europe and North America.
- CHAdeMO: Developed in Japan, CHAdeMO is primarily used for DC fast charging and is popular in Japan and other parts of Asia.
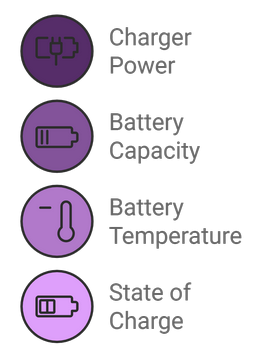
Charging Speeds
The speed at which an EV can be charged depends on several factors, including:
- Charger power output: Measured in kilowatts (kW), the higher the power output, the faster the charging speed.
- Vehicle battery capacity: Larger batteries take longer to charge.
- Battery temperature: Cold temperatures can slow down charging.
- State of charge: As the battery nears full capacity, charging speed typically slows down.
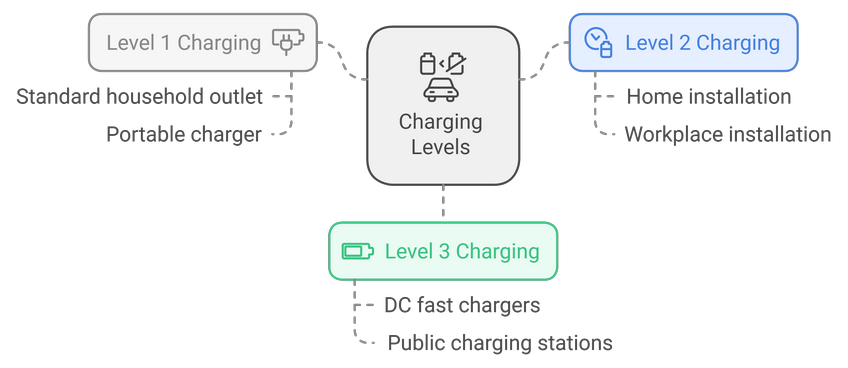
Charging Levels
Charging levels are used to categorize charging speeds:
- Level 1 Charging: The slowest type of charging, using a standard household outlet and a portable charger.
- Level 2 Charging: Faster than Level 1, often installed at home or workplaces.
- Level 3 Charging: The fastest type of charging, using DC fast chargers found at public charging stations.
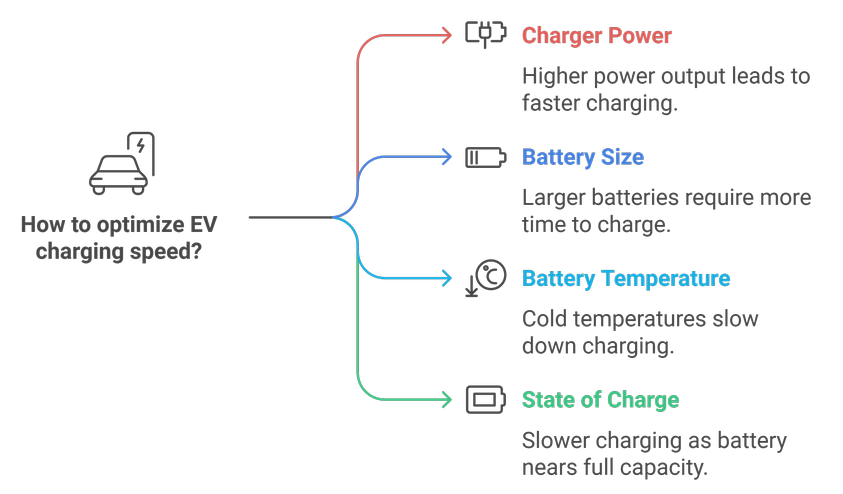
Factors Affecting Charging Speed
Several factors can influence the charging speed of an EV:
- Charger power: Higher power output results in faster charging.
- Battery size: Larger batteries take longer to charge.
- Battery temperature: Cold temperatures can slow down charging.
- State of charge: Charging speed slows down as the battery nears full capacity.
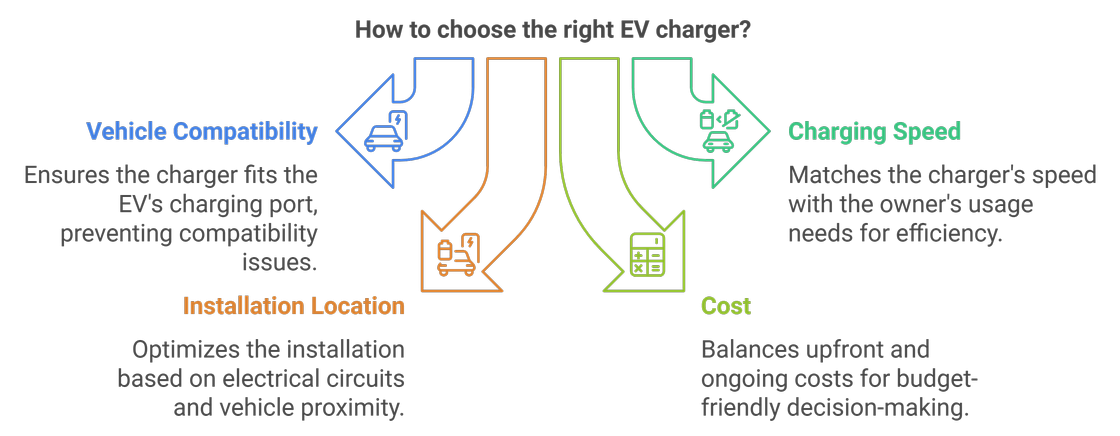
Choosing the Right Charger
When choosing an EV charger, consider the following factors:
- Vehicle compatibility: Ensure the charger is compatible with your EV's charging port.
- Charging speed: Determine the desired charging speed based on your usage.
- Installation location: Consider factors such as available electrical circuits and distance to your vehicle.
- Cost: Compare the upfront costs and ongoing operating costs of different chargers.
Additional Topics of Interest
Would you like to know more about a specific aspect of EV charging, such as installation costs, home charging solutions, or public charging networks? Here are some additional topics you might be interested in:
- Home charging solutions: Benefits of home charging, installation tips, and available options.
- Public charging networks: How to find charging stations, membership options, and payment methods.
- Charging infrastructure: The role of government policies and industry initiatives in expanding charging networks.
- Battery technology: Advances in battery technology and their impact on charging times.