Common Challenges with Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure and Availability
FAQ

Common Challenges with Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure and Availability
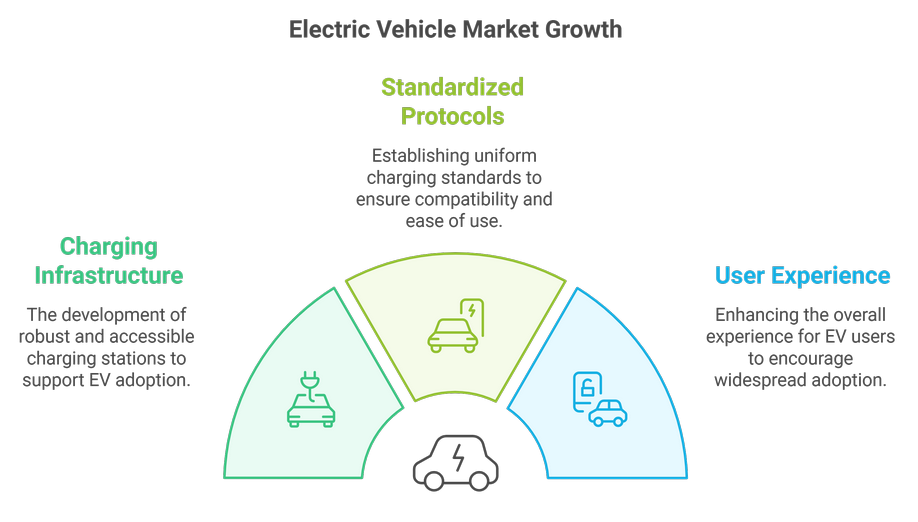
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular as a sustainable transportation option, but several challenges related to charging infrastructure and availability hinder their widespread adoption. This document outlines the key issues faced by EV users, including limited charging stations, inconsistent charging speeds, and the complexities of charging processes. By addressing these challenges, stakeholders can facilitate the growth of the electric vehicle market and promote a more sustainable future.
Limited Charging Stations
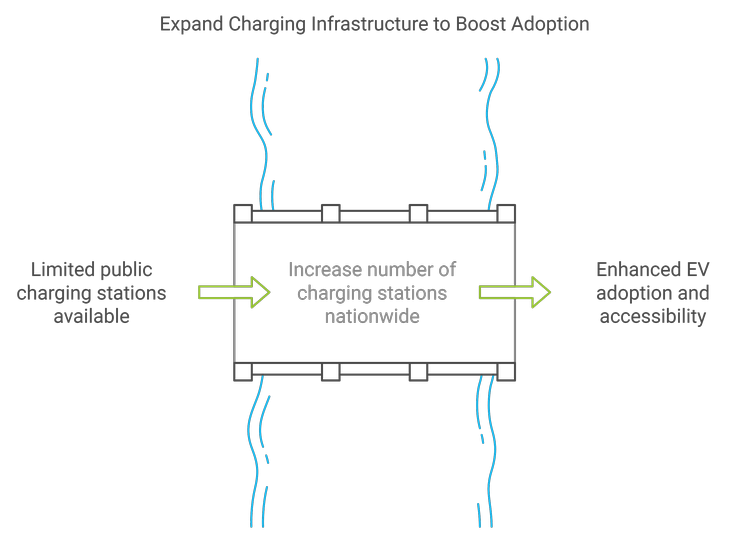
One of the most significant challenges is the shortage of public charging stations. This issue is particularly pronounced in rural areas and regions outside major cities, where access to charging infrastructure is limited. As a result, potential EV owners may hesitate to make the switch due to concerns about charging availability.
Inconsistent Charging Speeds
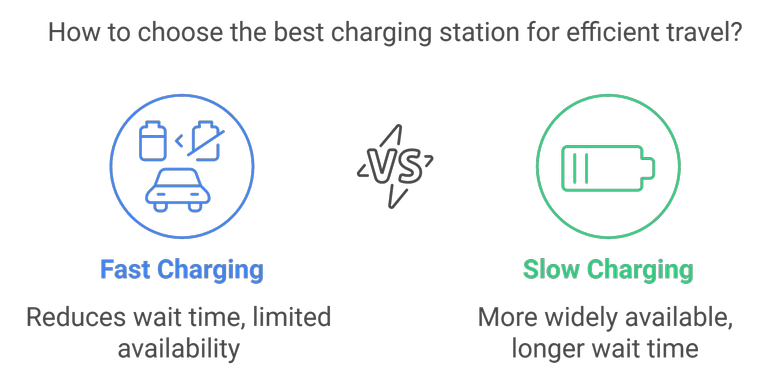
Charging speeds can vary widely between different charging stations. While some stations offer fast charging options, these are often limited in number. This inconsistency can lead to frustration for EV users, especially during long trips when quick charging is essential.
Lack of Standardization
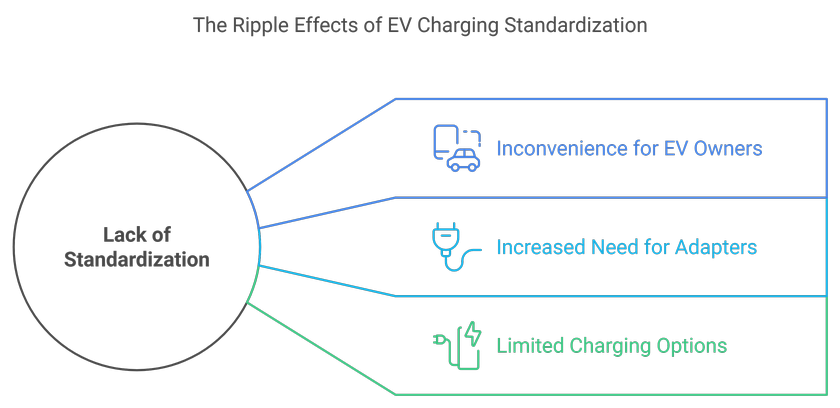
The absence of standardization in charging connectors and protocols complicates the charging process. Different manufacturers may use varying standards, making it difficult for EV owners to charge their vehicles at various locations without the need for adapters.
Charging Time
Charging an electric vehicle can take several hours, particularly for larger battery packs. This long charging time can be inconvenient for users, especially during long-distance travel. Additionally, range anxiety—the fear of running out of battery power before reaching the next charging station—can deter potential buyers from choosing an EV.
Cost
The initial installation costs for home charging stations can be significant, particularly if additional electrical work is required. Furthermore, while some public charging stations offer free services, many charge fees that can add to the overall cost of EV ownership.

Grid Capacity
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles could strain the existing electrical grid, particularly during peak charging times. To accommodate the increasing demand for EV charging, utilities may need to invest in upgrading the electrical grid, which can be a costly and time-consuming process.
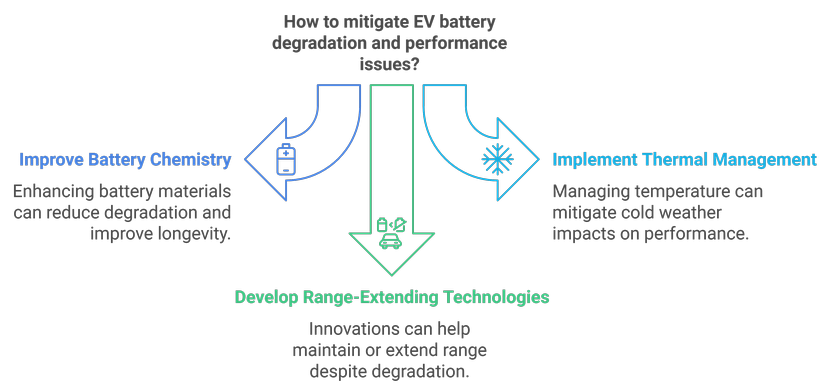
Battery Technology
EV batteries are subject to degradation over time, which can reduce their capacity and range. Additionally, cold weather can negatively impact battery performance, further limiting the range of electric vehicles in certain climates.
User Experience
The complexity of finding and using charging stations can be daunting for new EV owners. The lack of reliable real-time information on charging station availability and status can exacerbate this issue, leading to a frustrating user experience.

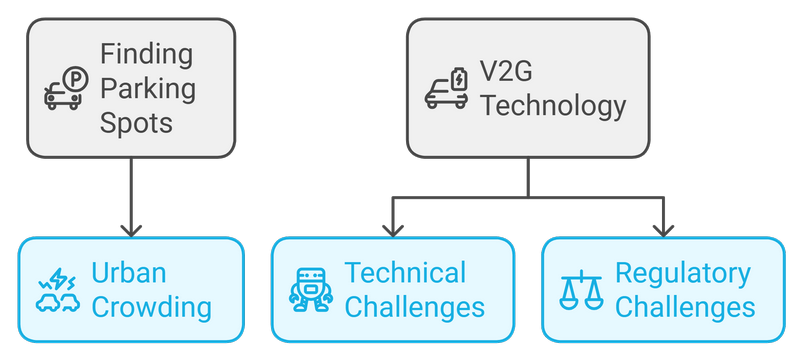
Other Challenges
Finding parking spots with access to charging stations can be challenging in crowded urban areas. Moreover, while vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology holds promise for enhancing energy efficiency, there are significant technical and regulatory challenges that must be addressed before it can be widely implemented.
Conclusion
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the continued growth of the electric vehicle market and the transition to a more sustainable transportation system. By improving charging infrastructure, standardizing charging protocols, and enhancing user experience, stakeholders can help facilitate the adoption of electric vehicles and contribute to a greener future.